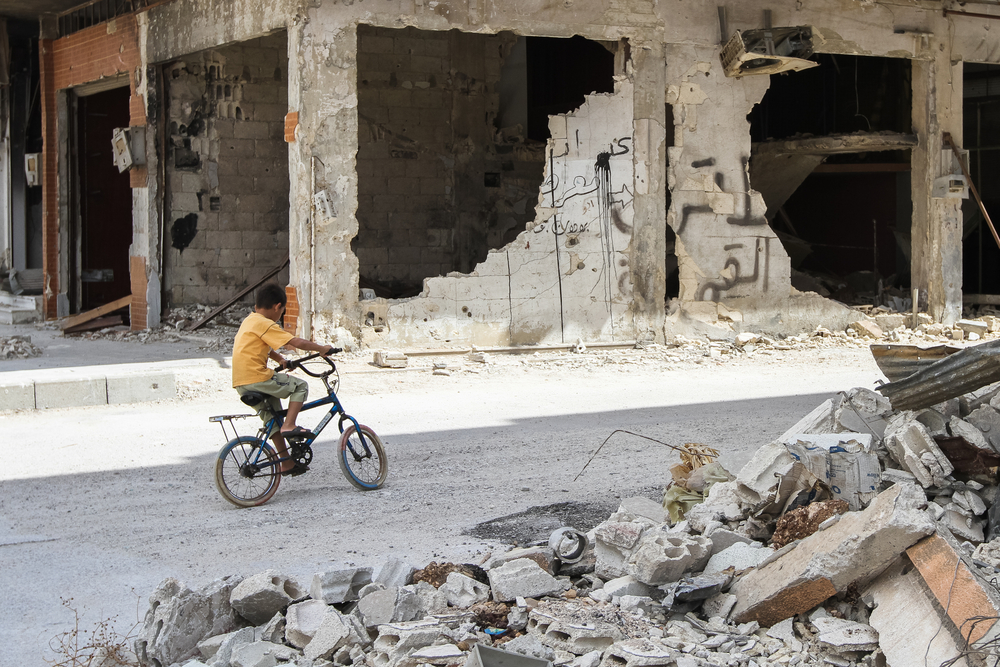
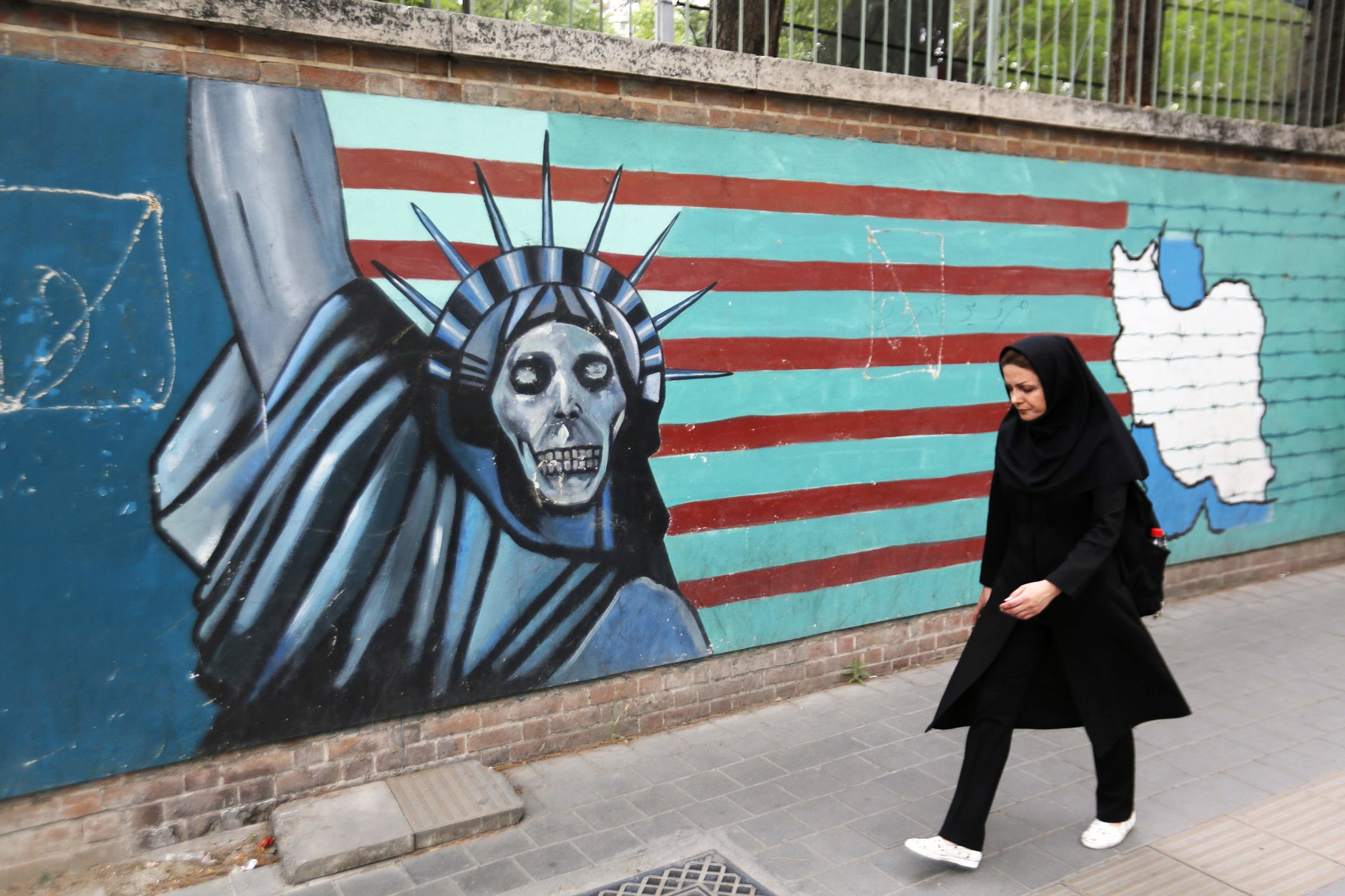
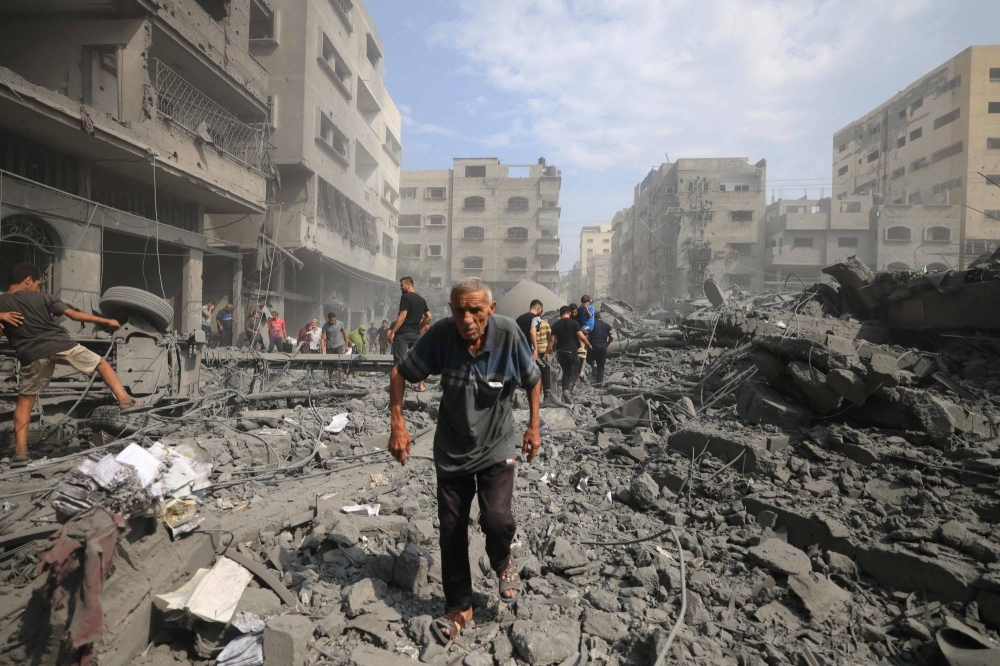
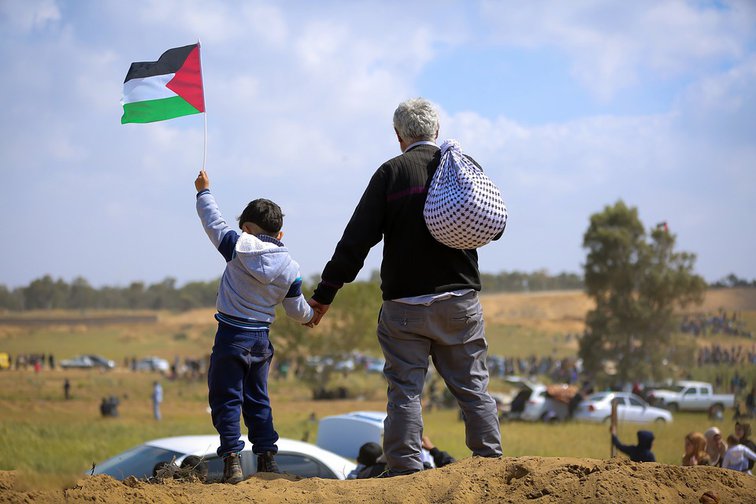
Nine years after the start of the conflict, Syrians still suffer war effects, lack of reconstruction, and economic crisis. Depressions and serious illnesses multiply, as so many symptoms of an impossible return to normal.
The initial democratic revolution, carried by the breath of the Arab Spring, turned into a war with multiple ramifications. Undoubtedly over 500,000 dead, tens of thousands missing, arrested, tortured in regime prisons, and millions of displaced people and refugees in Turkey, Lebanon, Jordan, or further afield.
The stigma of war
Today, this war is still raging in the province of Idlib, the last rebel entity in the country. But from Deraa, in the south, to Hassaké, in the northeast, the whole country continues to bear the stigma; collapsed buildings, mined fields, shut down factories, destroyed hospitals, and schools. War is everywhere, and is the first scene in the minds of people.
Food insecurity
Syrians had rationed gasoline and heating oil, and they are returning to the use of tickets for rice, sugar, oil, and tea. “A family is entitled to 4 kg of sugar per month at the subsidized price (250 LS) but must obtain supplies beyond that at the normal price (450 LS), and a small, trivial surgical operation costs three times the average salary,” says an Alepin.
Economic crisis
Elsewhere in Syria, the evidence gleaned agrees. Some of the Syrian families, who owned their homes, made some repairs. But we cannot talk much about reconstruction due to money issues.”With each military development, everything else slows down, and building priority is not even there: even in Damascus. People are mainly busy earning enough to buy their food.” Maher said, a 35 years old man living in Damascus.
Moreover, the international community with the hope imposed sanctions caused the collapse of the Syrian pound (LS). Nowadays, 1 dollar is exchanged for more than 1,200 pounds, almost three times the official rate set by the Central Bank.
The daily puzzle
A drop of water in an ocean of distress. The UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs estimates that 11.1 million Syrians (out of 17 million in total) need humanitarian assistance. About half of them are displaced people, forced to leave their homes.
Season changes, mainly Winter, and its freezing temperatures were particularly trying for them, whether they were crammed into camps, or overcrowded housing, they had no choice but to return home, to a building more or less destroyed.
A civil war with multiple ramifications
March 2011. First demonstrations in favor of democracy in Damascus, then in Deraa. Repressed by the regime, the protest turned into an armed rebellion. In July, the Free Syrian Army (ASL) was founded.
2012. The Democratic Union Party takes – with its armed wing, the People’s Protection Units (YPG) – control of the Kurdish regions.
2012 and 2013. The rebels supported by Turkey, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, the United States, and France, seized most of the North and East. The Islamist or Salafist groups are gradually supplanting the ASL.
2014. Daesh seizes almost half of the country and proclaims the “caliphate”. The mainly Kurdish Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) take over, its capital, Rakka, supported by the international coalition on October 17, 2017.
2015. Russia enters the conflict in support of the regime. The Syrian army is victorious in Aleppo (December 2016), Homs and Deir Ez-Zor (2017), Ghouta, and Deraa (2018), while waiting for Idlib.
Russia’s Intervention and the Process of Preparing the Constitution in Syria
Russia’s relations with Western imperialists were in their worst period after the Cold War. The expectation that Hillary Clinton would win the next presidential election led most of the diplomats in the region to assume that there would be limited cooperation between Russia and the USA in the foreseeable future in Syria. Thus, Russia became a key country for the future of Syria. This made Syria dependent on Russia. For example, the Syrian government is not the only political actor that determines the extent and duration of Iran’s presence in Syria. In addition, Iran is becoming more politically and economically dependent on Russia and China to the extent that it loses its chance to compromise with the US regime.
In 2015, while military developments continued in northern Syria, Russia took steps to prepare a new constitution in Syria. On December 19, the UN Security Council called for an urgent ceasefire; then a political negotiation process took place. In this framework, Russia quietly launched a constitutional process that guarantees its “presence” in the country. let’s say that Russia supported the Syrian regime to protect its strategic interests and to try to become an important political power in the Middle East while fighting against terrorism.
Russia’s relationship with the Syrian regime
During the Syria peace talks in Astana in January 2017, the Russian government announced a draft constitution for Syria. This draft constitution has been long spoken since Vladimir Putin announced that a new constitution is critical to finding a political solution to the crisis in Syria. Almost all opposition groups strongly opposed Russia’s proposal.
In response, Russia suggested that this draft was merely a “guide” for the peace process. According to the draft, Russia’s relationship with the Syrian regime was not only strategic but also carried an ideological content. Accordingly, Russia seemed to continue to block any Western plan to force Assad out of power. One of the most important consequences in Turkey and Saudi Arabia was directly affected by the draft-backed opposition.
In March 2019, the Syrian regime announced that the constitution should emphasize the country’s sovereignty. It is clear that a new constitution as a “political solution” is one of the main issues of Syria as well as the imperialists and their representatives in the Middle East.
For more Click
Is There Any Hope for Peace in Syria?
Like the communists of a country whose role we have described above in the Syrian tragedy, we want to underline several points for long-term peace in Syria and a wider region.
The main security threat in our region is NATO, the USA, and the forces that insist to cooperate with them. When all imperialists and occupying forces withdraw from this region, with the removal of their troops and paramilitary forces, peace in Syria will only take place. All foreign bases belonging to the imperialist countries in the region should be closed. Open or confidential, all imperialist agreements must be terminated. An egalitarian system based on the expropriation of assets and central planning should be established.
It is equally vital that peace in Syria should be established on a secular basis, without any superiority of any ethnic or religious group over others.
Only the Syrian people can decide on the future of Syria, and this right belongs only to them.
Also, Check



 Featured1 year ago
Featured1 year ago


 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago


 Featured1 year ago
Featured1 year ago

 Featured3 years ago
Featured3 years ago


 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago


 Featured4 years ago
Featured4 years ago


 Featured1 year ago
Featured1 year ago


 Featured2 years ago
Featured2 years ago



